
Trauma-Associated Disorders
Trauma, in its most general definition, is a state of discomfort resulting from an unusual experience that has a lasting effect on the individual’s mental state and personality. It is possible to examine traumas in 2 types as short-term and permanent traumas. While short-term traumas occur as a result of sudden and non-continuous events such as earthquakes, fires, and traffic accidents, continuous traumas include continuous situations such as domestic violence, neglect, abuse. The way of perceiving and making sense of the events or the catastrophic experiences that can create a traumatic effect differs for each individual. According to one person, the situation/event may be experienced by someone else as a traumatic situation, while it may reveal emotions that can be overcome. This situation is shaped by many factors such as the person’s developmental processes, genetic structure, and social environment.
Acute Stress Disorder (Asb)
Acute stress disorder is a condition in which people develop symptoms soon after exposure to a traumatic experience. According to the diagnostic criteria, it should last more than 3 days after the stressful event and should not exceed 1 month after the event. If symptoms persist for more than 1 month, it is not called acute stress disorder. Many of the people who continue to have problems afterward are diagnosed with post-traumatic stress disorder. Events such as serious injuries, sexual or physical abuse, death of a loved one are experiences that can cause acute stress disorder. But not every mourning process turns into trauma.
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder do not usually appear immediately after the trauma. After some time has passed since the traumatic event, people relive the event (flashback) and avoid thinking about the event. They may develop a sense of guilt by holding themselves accountable for what happened. Physiological arousal such as sweating, trembling, focusing difficulties, waking up from sleep and being alert all the time are common symptoms. Prolonged duration of the traumatic event, being a rare condition, and extreme severity increase the likelihood of individuals developing PTSD. At the same time, traumatic situations experienced by people in close circles such as children, spouses, relatives are also one of the reasons that increase the probability of developing PTSD.
Events that may be traumatic for adults may not be for children. In particular, the criteria for trauma before the age of 6 may differ markedly. Experiencing the event directly, especially witnessing or learning what happened to primary caregivers (mother, father, etc.) are situations that may lead to the development of PTSD in children. There is no re-experiencing of the traumatic event, that is, flashbacks, which exist in adults in the 0-6 age period. Because in this period, abstract thinking skills are not fully developed yet. Children may not remember the event, but they avoid evocative objects, people, and situations. When examining post-traumatic stress disorder in children, exposure to traumatic events through the media is excluded. Since the self-centered mindset is dominant at the age of 6 and before, the child only thinks about himself and his relatives, and the events in the media do not turn into trauma. Among the symptoms that a traumatized child may show are retroactive behaviors we call regression. If an 8-year-old child suddenly begins to show the developmental characteristics of younger years, trauma should be suspected. Negative memories may not appear to be distressing to the child, but may arise with re-enactment during play. Children may have difficulty in establishing relationships between events. In cases where they have not experienced the memory that caused the trauma before, they cannot easily express the event because it is difficult for them to perceive the event. For this reason, it is recommended that children who are exposed to situations that can be considered trauma should seek expert support immediately.
Posted by:
Psk. Deniz TAN KUMCUOĞLU
Uzman Bilgisi
Yazıları

Is There Such a Thing as Coronaphobia, or Not!
“What if I’ve contracted the virus?” “What if I’m asymptomatic and pass it on to someone?” “If I go outside, it will definitely find me.” “I won’t be able to protect my child.” “Have I washed my hands enough?” “I think I didn’t wash for 20 seconds; let me wash them again.” … Hundreds of …

What is Stress? Symptoms and Treatment Methods of Stress
Stress, the natural reaction of the body during any moment of danger that requires adaptation or response, can be triggered by both real and perceived threatening situations. The observed situation of danger can be an actual event or a situation perceived as “dangerous” by the mind. The stress response that emerges to protect the individual …

Empathy: The Art of Understanding Others and Establishing Empathic Connection
The term “empathy” is briefly mentioned as “duygudaşlık” on the Turkish Language Association’s website, and in psychological sources, it is also referred to as “eşduyum.” The word “empathy” comes from the Greek word “empathia,” using the “em” prefix, which implies within or inside. “Pathia” means feeling, and thus, the word “empathia” gains its meaning as …

The Sense of Emotional Neglect
Emptiness The traumas individuals experience during childhood can leave profound marks on their lives. Neglect and abuse during childhood can lead to psychological problems in adolescence and adulthood. According to research, 35-57% of individuals may exhibit psychological symptoms in adulthood based on the neglect and abuse they experienced in childhood (Goodman, Rosenberg, Mueser, & Drake, …

Healthy Communication in Marriage
Effective Ways to Solve Problems in Marriage – How Should Healthy Arguments Be? Marriage is the union of two individuals with distinct personality traits, cultural backgrounds, perspectives, values, and beliefs, creating a structure where they rediscover themselves. During this process, adaptation and harmony become fundamental qualities. Considering that each person tries to adapt to their …

Bedwetting (Enuresis)
The term enuresis comes from the Greek word “enourein,” which means “to urinate.” Today, enuresis is used to describe the involuntary and inappropriate urination at an age when developmental control of urination is expected. Studies on urination indicate that Turkish families do not express much concern about enuresis. In addition to preferring observation or traditional …

Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) in Children
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) in children is characterized by the constant and often prolonged repetition of certain movements or thoughts. Obsessions are recurring, disturbing, illogical thoughts, urges, or images that are recognized as unwanted but are resistant to efforts to distance oneself from them. Compulsions, on the other hand, are behaviors that emerge to reduce the …

Fear, Anxiety, and Children
Fear, Anxiety, and Children Many children experience fear and anxiety as a normal part of their development. They exhibit similar fears at similar ages, and these fears tend to change as they grow. Fears such as fear of animals, spiders, water, darkness, and supernatural beings can emerge from early childhood. As children enter adolescence, concerns …

Neurodevelopmental Disorders
Neurodevelopmental disorders encompass a group of differences and disorders that affect the development of the nervous system, leading to distinct functioning of the brain. Children with neurodevelopmental disorders may encounter challenges in language and speech, motor skills, memory, learning, impulse control, and social skills. The effects of neurodevelopmental disorders tend to persist throughout a person’s …

The Importance of Self-Care: Prioritizing Yourself and Self-Care Practices
Taking care of oneself is a vital behavior to maintain our physical, mental, and emotional well-being. In the hustle and bustle of daily life, when we prioritize the needs of others before our own, there may be a tendency to neglect our own needs, adversely affecting our lives. However, paying attention to our bodies, health, …

Psychological Resilience: The Power of Coping with Challenges
When we talk about psychological resilience, negative events usually come to mind first. However, throughout life, despite experiencing many events that cause anxiety, stress, and concern, these are not always negative or unwanted situations. Sometimes, even when eagerly awaited, certain situations can be challenging when they occur. Therefore, psychological distress does not only lead to …

Depression and Work Performance: How to Cope with Depression in the Workplace?
Depression, under the concept of melancholy, has come as one of the oldest terms in the realm of mental disorders. Hippocrates explained the biological origins of depression, suggesting its connection to an increase in black bile around 400 BC (Türkçapar, 2009). Complaints associated with depression can manifest in various forms, including disturbing mood, changes in …

Anger Management: Path to Achieving Healthy Inner Balance
Anger is a powerful emotion that all of us experience from time to time. It is a understandable reaction to various triggers such as disappointment or perceived injustice. While anger itself is not inherently negative, how we manage and express it can significantly impact our relationships, mental health, and overall quality of life. While anger …

From Yesterday to Today: Sexual Myths
As living beings, we require various resources to sustain our lives. In order to identify human needs, various studies have been conducted, and in 1943, Abraham H. Maslow introduced the “Hierarchy of Needs” into the literature. The hierarchy of needs consists of 5 levels, and Maslow argued that we move on to the next level …

What is Speech and Language Therapy?
Speech and language therapy is a therapeutic approach used in the prevention, assessment, diagnosis, and intervention of communication disorders. It assists individuals in improving their communication and language skills. Speech and language therapy can be applied to both adults and children, addressing various speech problems and communication disorders such as speech repetitions and partial speech …

Effects of Depression on Adolescents and Support During the Adolescence Period
Adolescence is a period of rapid and intense changes in young individuals, accompanied by hormonal changes as they search for their own identities. Consequently, increased questioning about life is observed during adolescence. Adolescents often experience feelings of unhappiness, loneliness, and helplessness during this period. Serious problems in controlling their anger are also noted. Sleep and …

Trauma: Is it Possible to Erase Painful Memories?
From the moment we are born, we seek to understand and make sense of the world around us. Frequently, especially during certain age groups of our children, we hear questions like “What is this? What is it for? Why does this exist?” All of these arise from our need for knowledge. When we learn something, …

What is Depression and Understanding Someone with Depression
Depression is a psychiatric disorder where individuals feel unhappy, pessimistic, worthless, guilty, and hopeless. It can be accompanied by sleep and appetite problems, fatigue, and a lack of sexual desire. People experiencing depression find it difficult to derive pleasure from life, feel disinterested even in activities they used to enjoy, and may also exhibit slowed …

Gambling Addiction and Its Treatment
Gambling disorder is characterized by the inability to control gambling behavior, leading to unwanted and persistent gambling activities that disrupt individual, familial, or occupational functionality. In recent years, with the increased use of the internet, gambling disorder has been observed to rise even more due to online gambling activities (Yeşilay, 2021). Gambling, briefly, is the …

What is Smiling Depression?
Smiling depression, also known as hidden or masked depression, is one of the subtypes of depression. Depression is a psychiatric disorder characterized by pessimistic thoughts, low mood, feelings of worthlessness, guilt, hopelessness about the future, unhappiness, an inability to enjoy life, and, often, disturbances in sleep and appetite. When we look at smiling depression, we …

Autism And Asperger’s Syndrome
Autism is a neurodevelopmental disorder whose symptoms begin to appear in early childhood. In recent studies, it is mentioned that this disorder occurs as a result of the interaction of both genetic and environmental factors. Among the most important symptoms of autism are inadequate communication skills, reluctance/inability to relate and interact with people, and repetitive …

Winter Depression
Also known as winter depression, seasonal affective disorder or seasonal depression; It is a psychological disease that is triggered by the change of seasons, especially in autumn and winter, where the interest and desire of the person decreases, his thoughts, feelings and behaviors are negatively affected. Lack of sunlight, low temperatures, short days and being …

Childhood Masturbation
Masturbation behavior is an extremely natural and healthy process for the development of children. Children start to touch their own bodies in a way that they enjoy from an early age when they start to explore their bodies. This behavior is more common in children between the ages of 3 and 6 years. The child, …

Toilet Training in Children
Toilet training is an extremely important step in the growth and development processes of children. This process can be quite critical and sometimes worrying for parents as well as children. It is generally thought that children show interest in toilet training when they turn 24 months, but this period may be earlier or later in …

Study
The subject of study is one of the problems that the child and the family have in common. This is due to the differences between the expectations of the family and the child. The openness of the scissors in the disagreement here is much wider as a result of the reluctance of both sides to …

Growing by Playing – I Played, I Play, I Will Play!
The Importance of Play in the Developmental Perspective and the Stages of Play “We don’t stop playing because we grow old, we grow old because we stop playing” George Bernard Shaw Play is the most important source of spending time in a child’s life, a means of getting to know the environment and the world …

Online Classroom Kids
Online Education in the Covid-19 Process The pandemic has changed many systems around the world or caused systems to be recreated and all rules to be rewritten. The education system is perhaps one of the branches on which the pandemic has been most effective. The fact that education could not be carried out face-to-face due …

Don’t Deliver Bad News
What is bad news? How does the news affect the field? How does it affect the reporter? 1995 World Medical Association Declaration of Patient Rights, Article 7; talks about the right to be informed. In 1998 Turkish Medical Deontology Regulation, Patient Rights Regulation, Article 3/15; speaks of this right. Bad news negatively affects the individual’s …

What is Anorexia Nervosa (AN)? What are the symptoms and treatment
Anorexia Nervosa is an eating disorder with symptoms such as refusal to maintain a normal weight for age and height, excessive fear of gaining weight, disturbance in body image, and cessation of menstruation. An intense fear of gaining weight is at the root of anorexia nervosa, accompanied by a refusal to even maintain a low …

Meditation and Mental Peace: Methods to Calm and Focus the Mind
Meditation is a term that corresponds to the concept of “deep thinking” in the dictionary sense. In dictionaries, the word meditation is defined as “inner peace of the individual, calmness”. Meditation is a spiritual purification technique in different cultures and religions. Thanks to concentration and alertness exercises, the individual rests his mind and soul. One …

Healing with Art
Art can also be used as a way of expressing our trapped emotions. We relax our souls by expressing the feelings and memories that we have difficulty in putting into words with various branches of art. It works to solve any problem, including unhappiness, couple and family problems, trauma, anger, separation pain, grief and loss, …

Anxiety in Children
According to TDK, anxiety; Sadness has been defined as a state of tension of unknown origin that occurs with worrying thoughts. In the Dictionary of Psychology Terms developed by TDK, anxiety; It is characterized as unsettling feelings and thoughts that appear when a strong desire or impulse seems to be unable to reach its goal. …

Stop Rumination!
Rumination: It is mental occupation with negative content. In psychiatry, rumination is known as mental rumination: It is the repetitive and rigid repetition of negative thoughts in the mind without change. “These events always find me, why did they do this to me, what did I do to deserve this,” pondering over the cause of …

Why Is Life After Trauma Divided Into Before And After?
People who have been traumatized have been faced with a situation that has challenged their capacity to produce solutions until now, in a way they have never encountered before, and that shakes their selves. That’s why for them, life is divided into pre-traumatic and post-traumatic. The stress hormone of people who have experienced severe trauma …

The Effects of Parental Attitudes on Our Present Adulthood
Based on the cases I have encountered as an adult psychologist, I can say that; It is a subject that is frequently asked, trivialized, and can lead to significant changes if noticed. Let me explain with examples: If parents are overly controlling about their children’s body sensations and choices; Let’s say the child is not …

I love a lot! I Hate That So Much! “Ambivalence”
“I am not worthy of being loved anyway, no one I care about has valued me as much as I wanted/expected. I’ve never felt fully loved, exactly where I belong. Whenever I gave value in my relationship, the other party always abused it. I loved, I loved without giving up. When I love, I truly …

Child Longing
Having a child is seen psychologically as a “rite of passage to adult life”, “a fundamental part of sexual identity”, “the main purpose of marriage”. However, about -15% of couples of reproductive age have trouble conceiving. The condition called inability to have children, infertility or infertility is defined as the inability to become pregnant after …

Toxic Relationship
POISON OR LOVE? Why do we start a relationship? To be happy, to grow, maybe to find our other half and live in eternal peace. In fact, while our main goal is to feel better, some relationships have the opposite effect on us; it hurts and makes us feel bad. These kinds of relationships are …
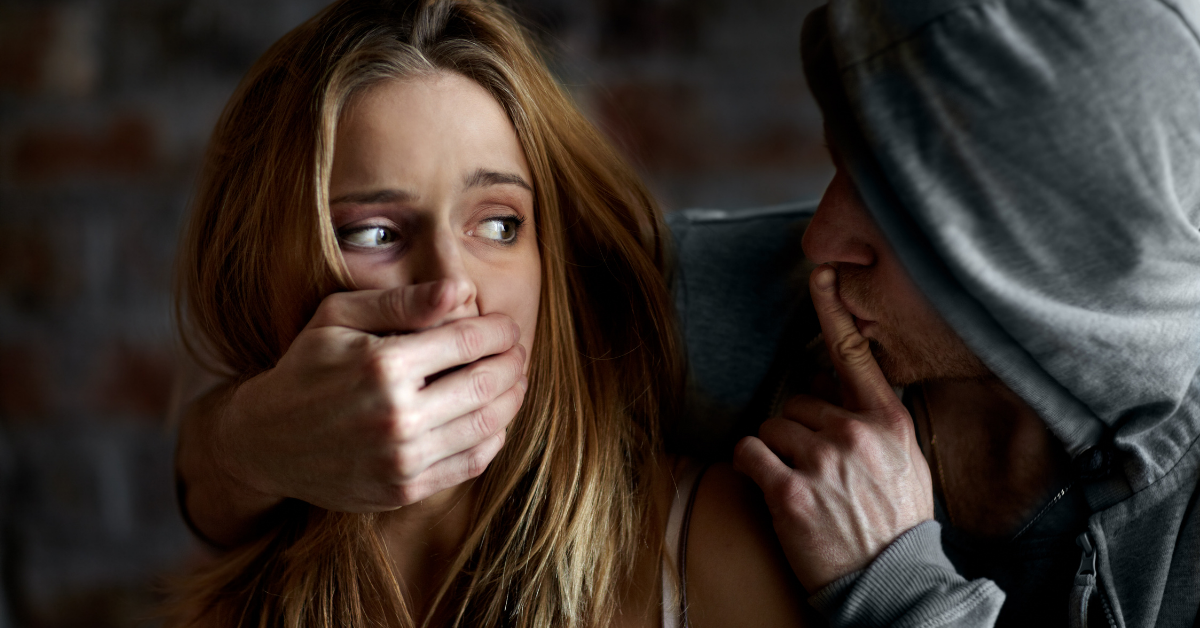

Stockholm Syndrome – Falling in Love with Your Executioner
While the first thing we look for in relationships is love, loyalty and respect, in some cases, people can develop positive feelings towards people who do not respect themselves, who behave badly, sometimes even torture them, and who use physical or psychological violence. In this situation, which seems abnormal from the outside, how can a …

Why Always the Same Scenario, Always the Same Ending?
The classic ending as a result of relationships: “Why do I always find people of the same type” . Look at destiny. It’s like people are changing, but what happened, the whole scenario is the same, you can’t find happiness or true love. It’s like a vicious circle… Do these people find you by chance …

The Classic End of Relationships
The classic ending as a result of relationships: “Why do I always find the same type of people” . Look at destiny. It’s like people are changing, but what happened, the whole scenario is the same, you can’t find happiness or true love. It’s like a vicious circle. Do these people find you by chance …

Are We Afraid of Marriage or of Ourselves?
According to the researches, the marriage rate in Turkey has decreased by ten percent in the last year. Years ago, when people’s biggest dreams were to get married, have a family and have children, how did we become so afraid of getting married? Do you ever think about the courage in arranged marriages in the …

Mood Disorders
How do our moods align with our emotions? They affect us every day. Sometimes we are sad, sad, and sometimes we are happy. We can even be sad and happy with a sudden change on the same day. Because every person’s life has its ups and downs, mostly due to external factors. In this case, …

Kids in Adults: Kids Mods
All of us from time to time “I acted like a child”, “I lost myself and I don’t understand how”, “when I remember it now, it was so ridiculous, how did I do it?” We have formed sentences such as: These sentences have a common feature; Emotions are quite intense and logic is quite in …

Trauma Body
“Learning to experience and tolerate deep emotions is essential for healing from trauma” (Body Keeps Records, Bessel A. Van Der Kolk). Trauma can be expressed as any kind of experience that harms a person’s mental and physical health. Therefore, sometimes trauma is a sudden and unexpected fear, sadness, and painful event; and sometimes it can …

Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
A self-fulfilling prophecy can be recognized in common language as “What I feared happened to me, I already knew it would happen”. Well, do you think it really happens to the person that he/she is afraid because he/she knows or because his/her intuition is high? Reply; No. Because the self-fulfilling prophecy does not arise from …
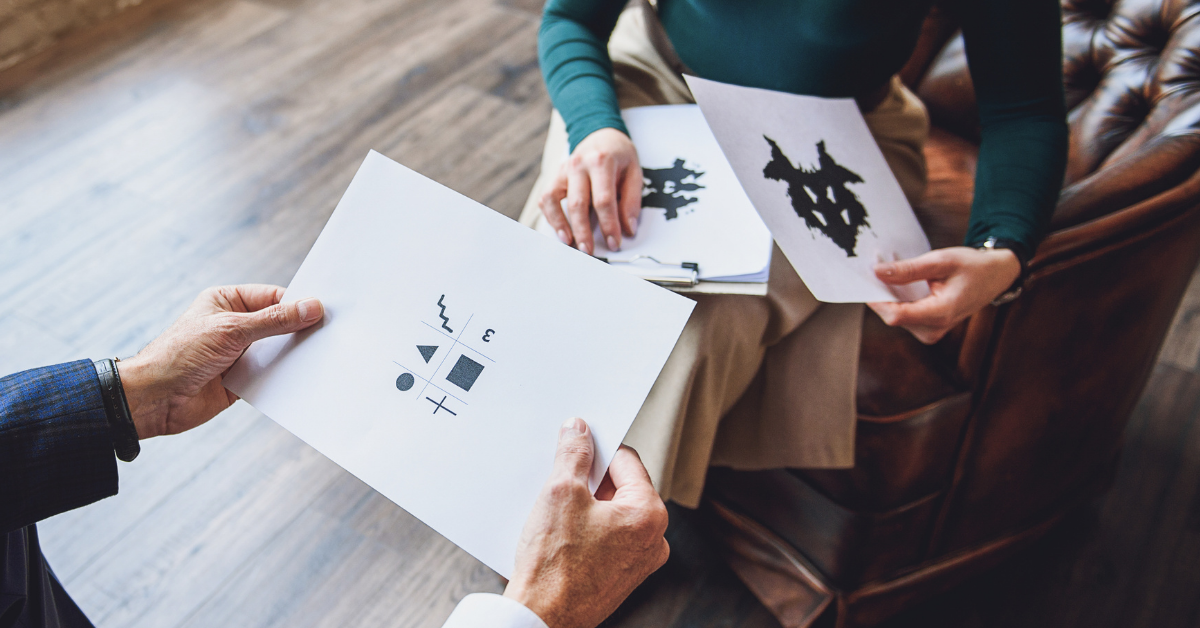

Auxiliary Element of Psychotherapy: Psychological Tests
Psychological tests, which are one of the methods that we use frequently in the clinic in order to get to know the individual closely, are measurement tools that allow the evaluation of a wide range of individuals, not only in a specific area. Although they are defined in different ways today, psychological tests are basically …
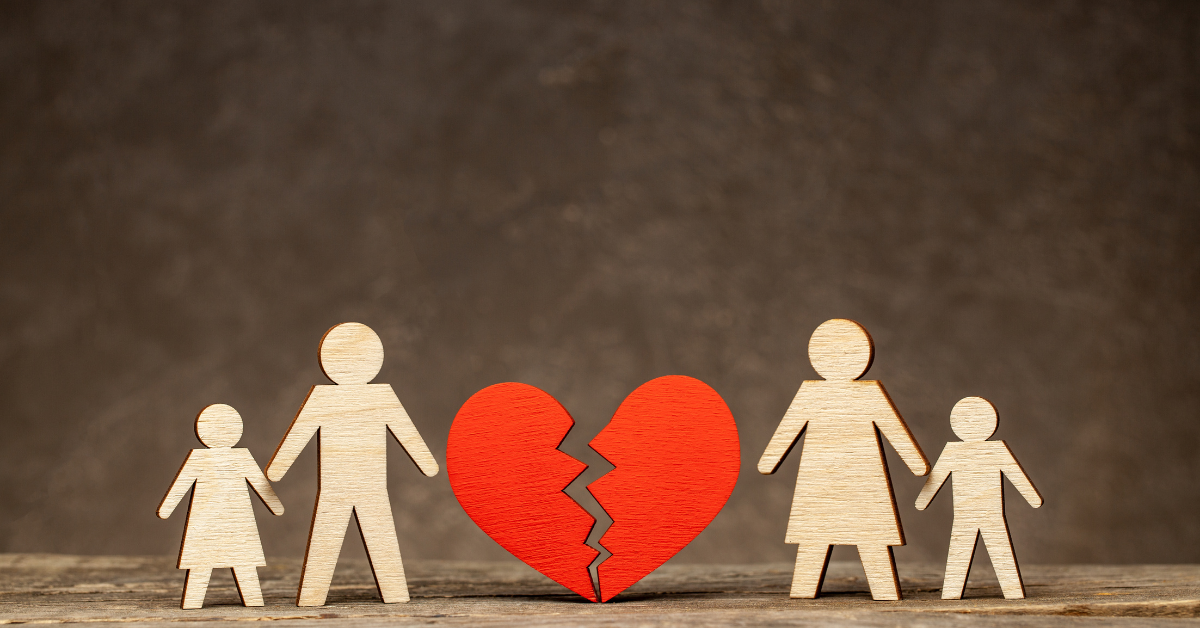

Effect of Divorce on Children
The process of divorce can show different psychological effects on children. The severity of these effects varies according to the age of the child, the way the child is informed about this issue, the communication within the family, the attitude of the parents, the mental state of the parents, the quality time spent with the …

What is Schizoid Personality Disorder?
Schizoid personality disorder is one of three personality disorders (the others are paranoid and antisocial PD). Diagnostic criteria in the latest edition of the DSM; dislike or unwillingness to enter into close relationships, including with family members; preferring activities in which they can be alone, showing little or no interest in intimacy with another person; …

Being a Mother
Being a mother is the most special process in human life that can experience all emotions at the same time. While many women can plan this process and prepare to become a mother emotionally, motherhood is a surprise for many women. Either way, it’s full of curiosity and anxieties. Motherhood is a state of great …

The Relationship between Sleep and Mental Health: The Importance of a Good Night’s Sleep
Sleep is among the basic physiological needs of living things. The purpose of sleep is to allow the body to rest and renew its energy. Sleep has an important role for the continuation of human life in a healthy way both physically and mentally. A quality night’s sleep helps to regulate the hormonal balance that …

Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Fear, anxiety, stress and tension are emotions that everyone experiences. Fear is a normal reaction to the threat of danger. Fear has the function of warning and protecting us in real danger. Sometimes fears can also be present in safe situations. Fear is of no use in this situation. When these fears are intense and …

What is Social Phobia?
Social phobia, also known as Social Anxiety Disorder, is a type of anxiety disorder in which a person has an extreme fear of social situations. This fear stems from the fear of being criticized, watched, and judged by others. Social phobia comes in two forms. The common type is common if the fears involve many …
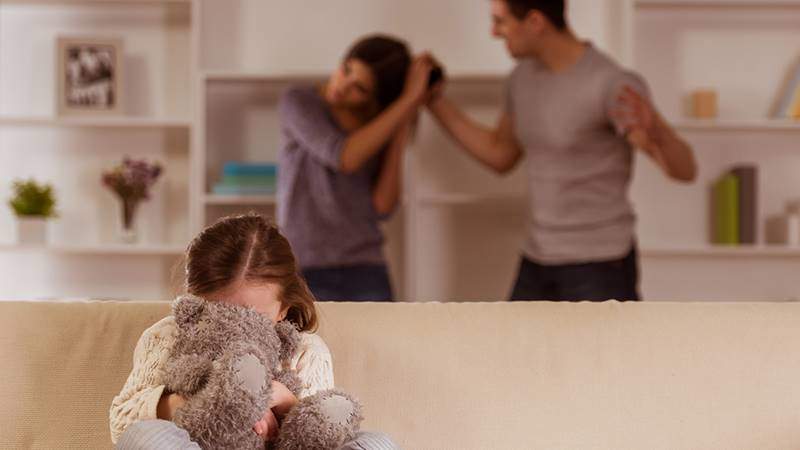

Domestic Violence
Are you being beaten? Are you scolded? Are you being banned? Are you bothered by your ex? Are you being forced into sexual intercourse or having your money extorted from you? Is your fiancee, spouse, ex-spouse, one of your children, or one of your family or friends responsible for all of this? Then you are …

Othello Syndrome
In the play “Othello”, written in 1603 by the English poet and playwright William Shakespare, the story of Othello, who thinks he has been cheated on by his wife and is jealous, is told (Shakespeare, 2008). The name “Othello Syndrome” started to be heard with an article published in 1955 (Todd and Dewhurst, 1955). Othello …

What is nomophobia? How Is Nomophobia Treated?
In recent years, thanks to technology, people can easily access all kinds of information. Depending on this situation, it is seen that individuals can do all their work very quickly and easily via telephone and internet. Individuals think that their work will be disrupted when they are away from the phone or the internet, there …

Eating Problem in Children
It is common for parents who complain that their children do not eat enough or less. Phrases such as “My child is playing with food instead of eating”, “My child eats his food very slowly”, “He refuses to come to the table at meal time”, “He says he is not hungry all the time, but …

The Suffering of Love
Emotional suffering; Although it is not a visible and tangible factor, it can be described as the emotional state that is experienced, that causes serious discomfort to the individual, and that the person has difficulty in describing. When describing this feeling, the person mostly tells it through his/her body. That is, “it’s such a pain…” …
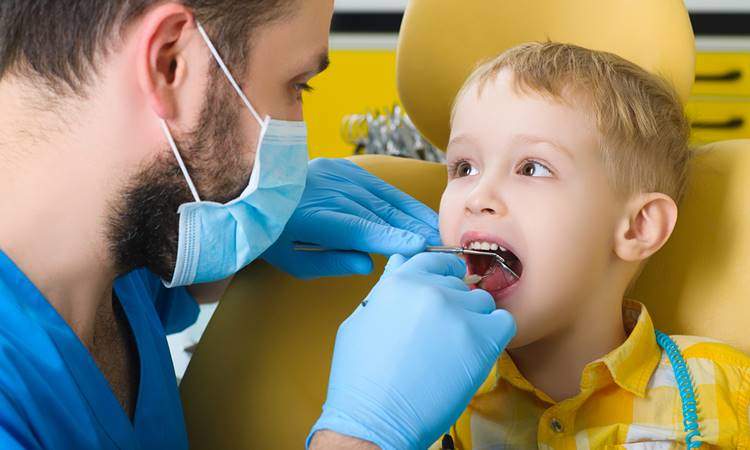
Advice for Those with Dental Chair Phobia
Fear of the dentist or dental health services is one of the important health problems seen in society. This is a very distressing situation for both the health worker and the person. Because the fear experienced causes the person to never go to the dentist despite having problems in oral and dental health, or not …

The Leading Role in These Loves Is Not Happiness, but Anxiety!
We all need love throughout our lives. Just as a child who receives love and attention grows up happily, when he becomes an adult, he may be aware that this need is met since childhood. The love we project is just as important as the love we need. Everyone can have a “love style”, but …

What is Sabotage in Romantic Relationships?
You’ve been seeing someone new for a while. Your communication is great, you have a great time, you are also very compatible sexually. You are starting to spend more and more time. But at the same time, a disturbing voice inside of you is constantly telling you, “It will go wrong soon and everything will …

What is Online Therapy? Things to Know Before Online Therapy
Since the 1980s, the widespread use of technology and internet all over the world has caused some life practices to change and transform. Accessing many services over the internet has enabled us not only to be limited to the facilities where we live, but also to not waste time. Since the beginning of 2020, every …

Why Do We Repeat Our Past Relationships?
Each of us has from time to time asked ourselves questions such as why do such people always find me, why do I have similar problems in my relationships, will it always continue like this. In fact, we repeat similar patterns in our relationships, even if it makes us uneasy or challenging. In relationships, we …

What Is Self Compassion and What Is It Not?
Self-compassion is an attitude and determines one’s attitude towards one’s own feelings and thoughts. It consists of three basic components. These are self-kindness, common humanity, and awareness. Self-kindness is related to what the person says to himself and how he acts after the events he has experienced. In other words, does the person criticize himself, …

What is a lack of self-confidence and how does it occur?
Movements of Confidence Come First, Feelings of Confidence Second! Self-confidence is an important concept for communication and self-expression skills in one’s life. It includes the person’s evaluation of himself. Self-confidence has an impact on one’s attitudes and behaviors by influencing the way people relate. A person needs the skills to establish and maintain relationships with …

Reflections of the Phenomenon of Racism to Today: The New Racism
Racism is a political ideology that emerged especially in the political field at the end of the eighteenth century and has deep ties to modernism as well as capitalist ideology. When we look at the dictionary meaning, racism is defined as the doctrine that suggests that one race is superior to other races by reducing …

The Balance of Screen Addiction and Online Education in Children During the Pandemic Process
Screen addiction The impact of screens on children is especially important right now. The rules set before the pandemic lost their effect with the extension of the time we stayed at home. The use of phones, tablets and computers, which became obligatory in the distance education process, also created addictions. In order for us to …

Suggestions for Students with Exam Anxiety
Recommendations to the Student: To reduce anxiety, apply ONLY to professional people (Psychologists, psychiatrists, psychological counseling and guidance specialists) and professional institutions (Turkish Psychological Association, psychiatry clinics). Thinking that it will increase your performance, the drug you will use may reduce your attention and give you drowsiness. As a result, your performance drops and you …

Obsession – Compulsive Disorder What is “OCD”?
(Obsessive compulsive disorder) Obsession-compulsive disorder is a mental disorder in which the person has obsessions, compulsions, or both and significantly impairs the person’s functionality. In this mental disorder, compulsive, intrusive thoughts and compulsions, repetitive behaviors and intellectual pursuits are seen. These cause great distress to the person and negatively affect their functionality. The person is …

Perfectionism, “All or Nothing”
Personality Personality is a concept that varies from individual to individual. The characteristics that an individual is born with and acquired through environmental factors form the personality. It is known that especially the first fifth and sixth years of life are important when personality is formed. Perfectionism Perfectionism is one of the personality traits. According …

How Does Childhood Attachment Affect Adulthood?
Attachment can be defined as “the close emotional bond between two people”. Attachment begins in the first moments of life. The bond established with the caregiver in the first 3 years of life is critical for the emotional relationships that the person will establish in later years. Thanks to sensitive care and physical comfort, a …

“Mature Children”: Children with Internalized Symptoms
Most adults have expectations that their children/students are “mature”. In fact, parents who have more than one child commonly make comparisons that one is “more mature” than the other, even when describing their children. When adults are asked to elaborate on the concept of “maturity” that they want their children to have, they say, “She …

Perfectionist Structures of Individuals and Parenting
The concept of perfectionism can be briefly defined as the effort of individuals to be the “best” in every field. Sentences that end with -should, -property that individuals put on themselves may actually be a result of their own perfectionist nature. This effort is about being perfect and being complete, 4/4. The effort to be …

What is Borderline Personality Disorder?
Borderline personality disorder; It is a psychiatric disorder that can cause problems in one’s social relations, thoughts, feelings and behaviors. The word ‘borderline’ means ‘on the border’. This disorder usually appears in adolescence or young adulthood. Borderline personality disorder usually manifests itself with fluctuations in the person’s emotions and behaviors towards the individuals around them. …

When Should I Go to a Psychologist?
What is psychotherapy? Psychology, in its broadest definition, is known as ‘the science of human behavior and mental processes’. The point to be noted here is the word ‘science’. Although psychologists focus on behaviors and mental processes, they explain the underlying causes and results of these issues on a scientific basis. Although the concept of …

The Effects of Parental Anxiety on the Child’s School Motivation
Parents may be concerned about their school-age children from time to time for various reasons. In this case, extreme reactions may also occur in children. These reactions can be seen as a general decrease in motivation or the child’s self-pressure and perfectionism. In any case, this situation, which may cause negative effects for the child, …

Reflection of Psychology on the Body: Somatic Symptom Disorders
Somatoform disorders, or somatoform disorders, are excessive preoccupations with physical symptoms or one’s health, although they do not have any medical equivalent. These disorders have a wide variety of classifications such as somatic symptom disorder (somatization), illness anxiety disorder (hypochondriasis), conversion disorder (conversion), and factitious disorder. Thoughts about bodily symptoms or being sick can be …

Our Child Brides Who Have Their Lives Taken From Their Hands
I have been dealing with issues involving child abuse, neglect and abuse since 1986. I think that marrying a child at the age of 13-14 to a person who is much older than him, who is the age of his father, uncle or even his grandfather, would constitute both neglect and abuse of the child, …

Children Are Afraid Adults Too
“This young, beautiful and excited woman has been unable to talk to strangers for some reason lately and has been afraid that she will start to stutter. I don’t know where this fear came from. This world fear and excitement gradually formed an important part of the personalities in our family, although it manifested itself …

A sense of belonging, ownership
The morning sun radiates light and sweet warmth with its rise. This light and warmth makes us watch the emergence of a magnificent work by fusing all the beauty of nature with each other. Nature moves in harmony with all its colors, no color excludes the other. They are all there to make each other …

Who is a Child and Adolescent Psychiatrist?
How does a child and adolescent psychiatrist work? In recent years, awareness of psychiatric and psychological problems has started to increase in the society, and it has been realized that psychology is one of the most important areas in human life. With the increase in awareness and the expanding scientific literature, it has been understood …

The Forbidden Apple and Cognitive Evolution
A common event is mentioned in all monotheistic religions; The expulsion of Adam and Eve from heaven… Accordingly, God says to Adam and Eve, “You can do whatever you want, but I forbid you to come near that tree.” Hearing this, the devil does his devil again and convinces Adam and Eve to approach the …

What is Vaginismus? What is not?
vaginismus; It is a psychological disorder that occurs as a result of the contraction of the muscles at the entrance of the vagina (female sexual organ), characterized by the anxiety caused by the perception of pain, and resulting in difficulty during sexual intercourse or the inability to have sexual intercourse. Although it is thought that …

Species Happiness is Possible in Partnership
Consciousness: Consciousness is the awareness of oneself, of one’s experiences, of his environment, of other people, and of the universe in which he lives as a whole. So, as ‘conscious’ individuals, are we really aware of ourselves, our environment and the universe we live in? If our sun were the size of the dot at …

Panic Attack
A panic attack is an unexpected, spontaneous condition accompanied by palpitations, sweating, tremors, feeling short of breath, chest pain or tightness, dizziness, lightheadedness, numbness, tingling, and an intense fear of death, fainting, or going crazy. . People with panic attacks apply to the emergency services of hospitals with complaints such as “I am having a …

Approach to a Child with Autism
Autism is a developmental disorder that presents with findings such as limitation in social interaction, significant delay in communication level, limitation in interests and repetitive behaviors in children. This disorder usually begins to show signs before the 36th month, and it is 4 times more common in boys than girls. While the incidence of the …

An Unhappy Child Who Never Grows Up: Peter Sellers
From the moment we enter the movie theater, we step into a new world in the magical atmosphere of 7th art. At the door of the hall, the fights of daily life are left behind and we find ourselves in completely different lives from the moment the movie starts. We can be rich, poor, full …

What is Depression? What are the symptoms? How is the treatment?
The term ‘depression’ is one of the most used medical terms in daily life, for this reason; It has been the subject of many misunderstandings and misconceptions. It is highly probable that almost everyone will hear the phrase ‘I am depressed these days’ from their mouths at some point in their lives. So, is every …

Depression May Not Come With Drums
Depression’s low mood, reluctance, not enjoying life, introversion, crying, irritability can often be easily noticed and may lead you to consult a psychiatrist with the thought of “Am I getting depressed?” However, depressive illnesses may not always begin to manifest itself by playing the drums and horns. That is to say, depression is actually a …

The Hate Diary of a Psychiatrist
The sickly color of the city turned pale and reduced the will to live in people. In fact, outsiders say that the gloomy weather suits this city very well. For those who live here, it doesn’t really matter. They spend the day in the evening without complaining about each other’s same lives every day. My …

Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Psychotherapy; It is the general name of the techniques that aim to solve the cognitive, emotional and behavioral problems of individuals through verbal interviews with a trained professional and to protect and improve the mental health of individuals. Throughout the history of psychiatry, different types of psychotherapy have been developed in various periods, shaped according …

The Psychology of Attachment “I Can’t Live Without You”
I can’t live without him, we complement each other, I’m incomplete without him, I can’t imagine a world without him… These expressions, which we all hear or say personally in our daily life, may not be so innocent after all. Ranging from ‘I’m nothing without you’ to ‘it’s mine or the black soil’, these sentences …

Role Distribution in Life: Unloved
There are children who are not accepted, loved, and rejected by their mothers. They climb to their mothers, to love me, take care of me, take care of me. The more she climbs, the more the mother pushes, the more the mother pushes, the more the child clings to the mother. These kids cry for …

Attitudes of Parents in University Exams
University exams have increasingly become the nightmare of both young people and parents in our country. Many people who put all their hopes into these exams go into a serious stress environment before and after the exam. They are right. So it’s not an unwarranted stress. Children flock to psychiatrists at exam time. They have …

Mental Problems Disrupt Our Physical Health
Studies by scientists say that mental problems and related problems can lead to serious diseases in the body after a while. Examining the timing and course of certain diseases shows how connected we are to the people in our lives and how much we are affected by these relationships. The frictions, turmoil and disappointments experienced …

So Was It Time to Die?
I always thought of our country as one big family. Not every country is a family, but our country has always been a big family since the establishment of the Republic of Turkey. Although the population of this family increased very rapidly, new brides and grooms entered the family, some of them were our own …

People of a Huge Country Looking for Himself
I’ve been a curious person for as long as I can remember. I was like that in my childhood. I will never forget the day I started school. My mother had tied white ribbons to my braided hair hanging from both sides. It was as if I was knocking on the door of the world …

Loving Yourself
It is actually very difficult for a person to love and like himself because the beast inside us is insatiable. If we do three, he’ll want five more. Such is the nature of man, but if it were not so, we would all sit hand in hand. Nature probably knows these things better than any …
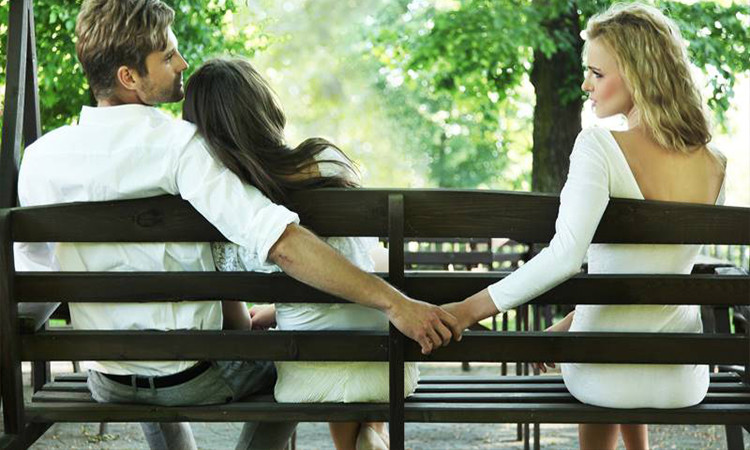

Betrayal
Betrayal is perhaps one of the greatest pains that human beings can experience in the world. Even poets, in poems and songs, are angry if you compare separation and betrayal with death, and they say that betrayal always hurts a person even more than death. Because in betrayal, there are infuriating and hurtful meanings such …
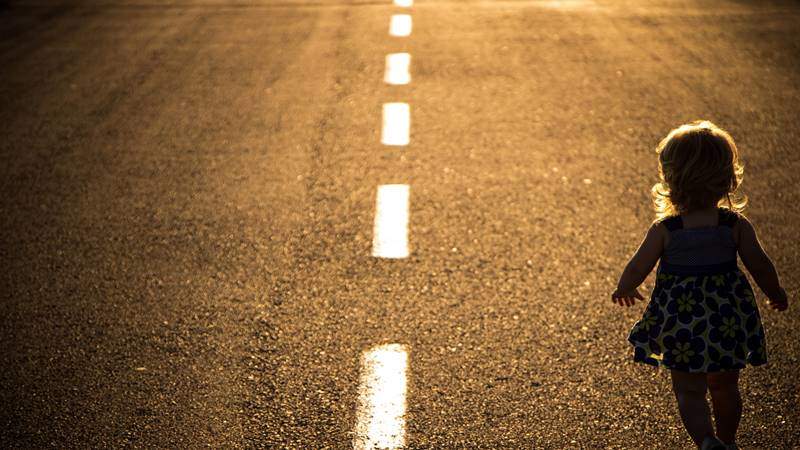

Always the Same Role
Our role in life begins the moment we are born. This first role, given to us by our mothers, fathers or very close relatives, sticks to us so much that we never leave that role as long as we live, even if the movies change or the scenarios are written differently. Then we call it …

Marriage, Middle Age, Lie
Usually all men are afraid before marriage. They flee as the prey flees the predator. They are afraid of being caught by the hunter. For a while, they see girls as husband hunters. They do not have such fears at a young age, long before the age of marriage. Then there is only love for …
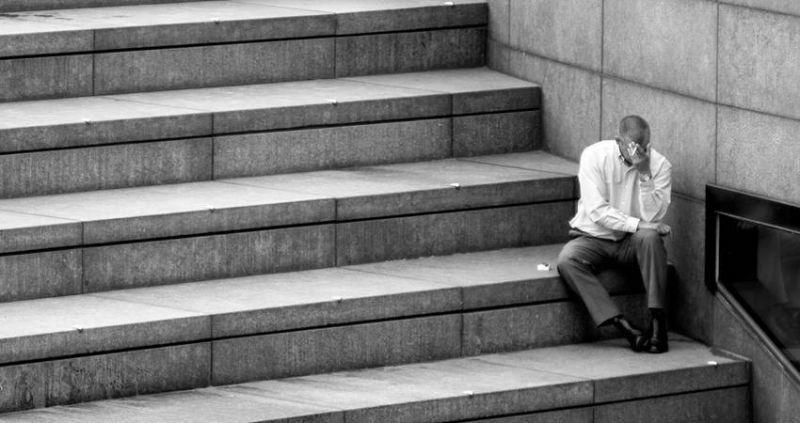

Reflections of the Economic Crisis on the Human Spirit
The people of our country have been living with crises for years. I mean, it never even came out. Economic crises that occur every 8-10 years, natural disasters, terrorism, emerging corruption and wars surrounding our country… All these strengthen our people against all kinds of crises and increase their ability to stand under all conditions, …

A Mobbing Tragedy
The meaning of mobbing can be defined as psychological violence, pressure or harassment. Especially in places where there is a hierarchical structure, it is the powerful oppressing the underdogs or harassing them in various ways. This harassment can sometimes be done by using social and psychological pressure methods, and sometimes it can be in the …

Trauma-Associated Disorders
Trauma, in its most general definition, is a state of discomfort resulting from an unusual experience that has a lasting effect on the individual’s mental state and personality. It is possible to examine traumas in 2 types as short-term and permanent traumas. While short-term traumas occur as a result of sudden and non-continuous events such …

Drug Uses in Psychiatry
We can say that there is an extreme tendency towards medical drugs in our society. Most of the time, it is common to use medication based on the symptoms that occur in the body, even if it is not prescribed by a doctor. In cases such as a small cough, fever or headache, we resort …
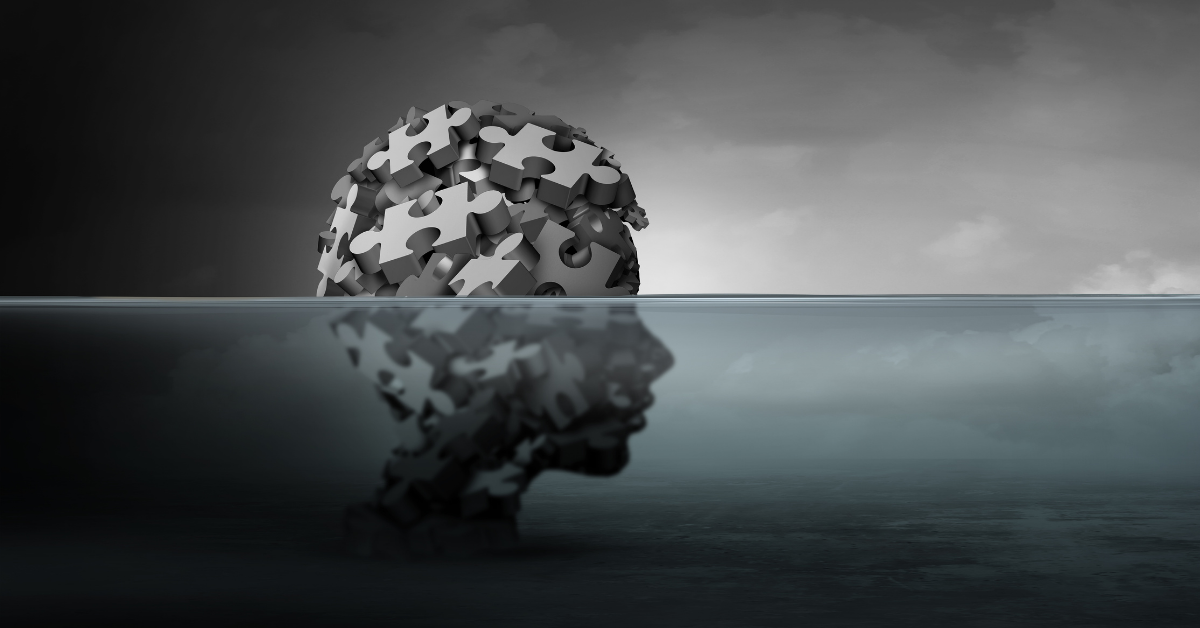

Our Most “Popular” Schemes
The emotional needs of individuals that are not met, especially in childhood, play a role in the formation of certain schemas. Emotional deprivation: It results from the emotional neglect of a child’s primary caregiver, most often the mother. The idea that “I will never be loved enough” prevails. These people, knowingly or unknowingly, put emotional …

The Importance of Peer Relationships in Children
In early childhood, babies begin to show a marked interest in all other children. However, since the social skills necessary to play with other children are not yet fully developed, the first types of play are the ones they play alone. After a while, they start to play side-by-side games with their peers around the …

Divorce: A Psychological Perspective
One of the most common issues that parents want to receive counseling or therapy services for their children is the divorce process. Divorce, which is an undesirable situation in parental relations, can lead to different effects for each family structure. Depending on the attitudes and behaviors of the parents, it can be considered normal, on …

Deception And Abandonment
In my first years of working as a cheating and abandonment psychiatrist, that is, 25-30 years ago (in fact, I don’t like talking about such huge numbers when talking about past years, but unfortunately this is the truth) I only listened to women who were cheated on. These were women stabbed in the chest, that’s …
Our Current Psychology Publications

Is There Such a Thing as Coronaphobia, or Not!
“What if I’ve contracted the virus?” “What if I’m asymptomatic and pass it on to someone?” …

What is Stress? Symptoms and Treatment Methods of Stress
Stress, the natural reaction of the body during any moment of danger that requires adaptation or response, can be triggered …

Empathy: The Art of Understanding Others and Establishing Empathic Connection
The term “empathy” is briefly mentioned as “duygudaşlık” on the Turkish Language Association’s …

The Sense of Emotional Neglect
Emptiness The traumas individuals experience during childhood can leave profound marks on their lives. Neglect and abuse …

Healthy Communication in Marriage
Effective Ways to Solve Problems in Marriage – How Should Healthy Arguments Be? Marriage is the union of two individuals …

Bedwetting (Enuresis)
The term enuresis comes from the Greek word “enourein,” which means “to urinate.” Today, enuresis …

Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) in Children
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) in children is characterized by the constant and often prolonged repetition of certain …

Fear, Anxiety, and Children
Fear, Anxiety, and Children Many children experience fear and anxiety as a normal part of their development. They exhibit …

Neurodevelopmental Disorders
Neurodevelopmental disorders encompass a group of differences and disorders that affect the development of the nervous system, …



